
- #ARCGIS API FOR PYTHON HOW TO#
- #ARCGIS API FOR PYTHON UPDATE#
- #ARCGIS API FOR PYTHON FULL#
- #ARCGIS API FOR PYTHON CODE#
In addition to the workspace, environments include the default output coordinate system, the default cell size for raster data processing, and several others. A workspace is one of several environment settings that influence geoprocessing operations.
#ARCGIS API FOR PYTHON FULL#
Instead of specifying the full path, you can set the workspace. Using only ambulances would return an error since there is no feature class named ambulances in the folder. Third, the feature class is referenced as ambulances.shp since the. This can result in unintended consequences when you use backslashes in strings. A backslash in Python is used as an escape character, which may change the meaning of the character following it. Also note that a forward slash (/) is used in the path instead of a regular backslash (\).

Second, the path is in quotation marks because it is a string. First, if you extracted the data to a different folder, you will need to modify this path. There are some points to note about the use of the path.
#ARCGIS API FOR PYTHON UPDATE#
If you saved the PythonStart folder to another location on your computer, you will need to update the path accordingly.
#ARCGIS API FOR PYTHON CODE#
Quotation marks in Python are always straight (as opposed to slanted). Both print("GIS is cool") and print('GIS is cool') are therefore correct, but print("GIS is cool') results in an error. Python uses both single and double quotation marks to identify strings, provided they are used consistently. You create a string by enclosing the characters in a pair of quotation marks. A string in Python consists of a sequence of characters. Most functions in Python have arguments or parameters, which are provided in parentheses following the function. A function in Python carries out a specific task. We can also create a histogram using the shape length field as input.In this line of code, print() is a function. We can use the HTML library to return the same output in a more readable way: The outcome looks like XML data inside a HTML file and is not very readable for humans. For example, the PopupInfo value of the first item can be accessed as follows: You can also access a separate cell value. Here, we print the column names and values of the first item: loc property can be used to subset entire rows, using the row´s index number, starting from zero. We can print the different column names as follows: For example, the shape function returns the amount of rows and columns of the entire DataFrame as a tuple: There are many functions to describe the data inside pandas DataFrame objects. The following pandas dataframe will be shown inside your Jupyter Notebook: It is not necessary to import the pandas library, as it one of the dependencies of the arcgis package, imported in the first line of code. Using the head function in the second line, we´ll only print the first five rows. We´ll now create a variable that holds the DataFrame object from the layer we´re interested in. Python returns only one item, so there´s only one layer (it is not displayed here to save space): We can reference this item as follows, in order to see how many layers it contains.

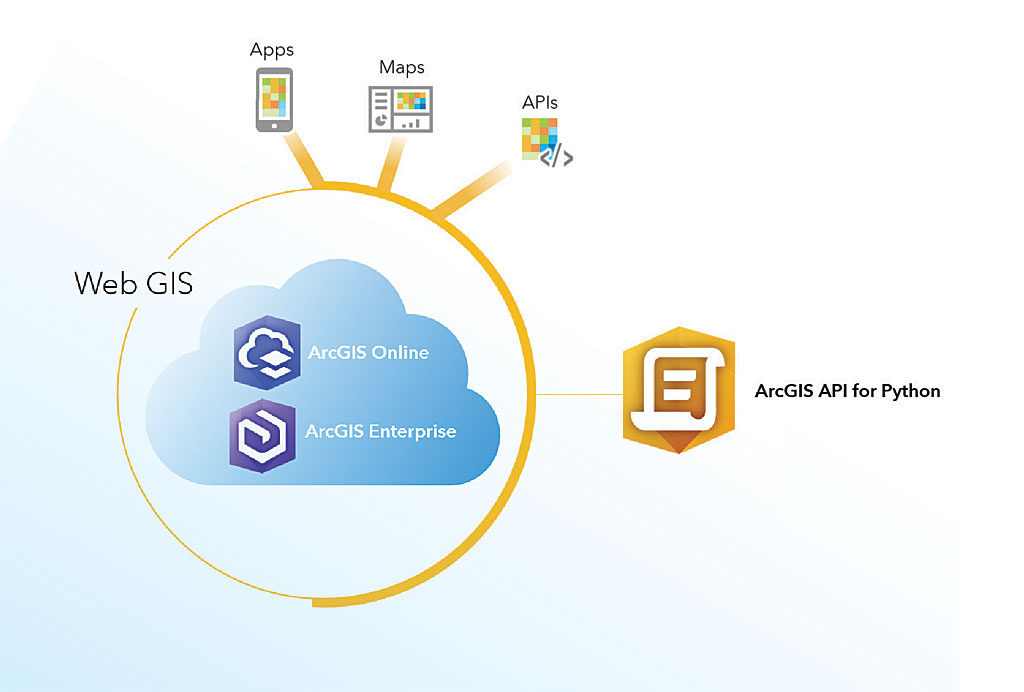
In: search_result = (query=”bruce trail”, item_type=”Feature Layer”, max_items = 5) We´ll search for a feature layer called “Bruce Trail” inside of ArcGIS Online: Make sure you have the latest available version of the API installed, which is version 1.3.įirst, we´ll login to ArcGIS Online using the Jupyter Notebook app:įeature layers are collections of layers containing geographical features as vectors. To follow the instructions, you can open a new Jupyter Notebook. Specifically, it uses pandas DataFrame objects that present data in a tabular form, comparable to Excel spreadsheets.
The ArcGIS API for Python uses the pandas library to display and edit attribute info. It works particularly well with Jupyter Notebooks, where you can also use bash commands, magic commands, plotting capabilities and take advantage of a nice overall presentation of code, visuals and comments. Pandas is a Python package for data manipulation and analysis. After searching and referencing spatial data, you the pandas library enables you to subset, describe and plot attribute data.
#ARCGIS API FOR PYTHON HOW TO#
This short tutorial covers how to use the ArcGIS API for Python and pandas DataFrame objects for displaying tabular data inside of your Jupyter Notebook application.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
